Petya ransomware impacting large organisations
Petya ransomware impacting large organisations in multiple countries.
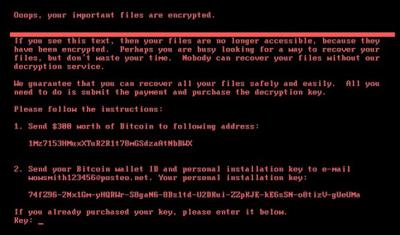
This new strain of the Petya ransomware started propagating on June 27, 2017, infecting many organisations. Similar to WannaCry, Petya uses the Eternal Blue exploit to propagate itself.
What is Petya?
Petya has been in existence since 2016. It differs from typical ransomware as it doesn’t just encrypt files, it also overwrites and encrypts the master boot record (MBR).
In this latest attack, the following ransom note is displayed on infected machines, demanding that $300 in bitcoins be paid to recover files:
How does Petya spread and infect computers?
Petya propagates itself by exploiting the MS17-010 vulnerability, also known as Eternal Blue. Symantec continues to investigate other possible methods of propagation.
Who is impacted?
At time of writing, Petya is primarily impacting organisations in Europe.
Is this a targeted attack?
It’s unclear at this time, however, previous strains of Petya have been used in targeted attacks against organisations.
Am I protected from the Petya Ransomware?
Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) and Norton products proactively protect customers against attempts to spread Petya using Eternal Blue. SONAR behavior detection technology also proactively protects against Petya infections. Symantec products also detect Petya components asRansom.Petya.
What are the details of Symantec's protection?
Network-based
protection
Symantec has the following IPS
protection in place to block attempts to exploit the
MS17-010 vulnerability:
• OS Attack: Microsoft SMB MS17-010 Disclosure Attempt (released May 2, 2017)
• Attack: Shellcode Download Activity (released April 24, 2017)
Antivirus
• Ransom.Petya
Symantec is continuing to analyze this threat and will post further information as soon as it becomes available.
ends


 Canterbury Museum: Mystery Molars Lead To Discovery Of Giant Crayfish In Ancient Aotearoa New Zealand
Canterbury Museum: Mystery Molars Lead To Discovery Of Giant Crayfish In Ancient Aotearoa New Zealand Ngā Pae o te Māramatanga: Māori Concerns About Misuse Of Facial Recognition Technology Highlighted In Science
Ngā Pae o te Māramatanga: Māori Concerns About Misuse Of Facial Recognition Technology Highlighted In Science Retail NZ: Retailers Call For Flexibility On Easter Trading Hours
Retail NZ: Retailers Call For Flexibility On Easter Trading Hours WorkSafe NZ: Worker’s Six-Metre Fall Prompts Industry Call-Out
WorkSafe NZ: Worker’s Six-Metre Fall Prompts Industry Call-Out PSGR: Has MBIE Short-Circuited Good Process In Recent Government Reforms?
PSGR: Has MBIE Short-Circuited Good Process In Recent Government Reforms? The Reserve Bank of New Zealand: RBNZ’s Five Year Funding Agreement Published
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand: RBNZ’s Five Year Funding Agreement Published



